Did you know that VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) 5.0 is now available for our VMware Cloud Services Providers. With this release, Cloud Services Providers can now take advantage of several important capabilities. In this short blog, we will highlight the key enhancements in deployment models, helping partners optimize their cloud investments.
Dedicated Private Cloud – Art of the Possible
In previous versions of VCF, the provider had to deploy a VCF instance per customer, which ran management components and workloads to maintain isolation. Because of this, there was a proliferation of VCF Consolidated architecture deployments requiring independent deployment and lifecycle management. However, with VMware Cloud Foundation 5.0, Cloud Services Providers can now leverage the VCF Standard architecture. Similar to previous versions of Cloud Foundation mentioned in last year’s blog and vmLIVE, CSPs can now deliver cloud services with improved operational efficiency while ensuring separation at the identity level as a fundamental aspect of isolation.
The Standard Architecture
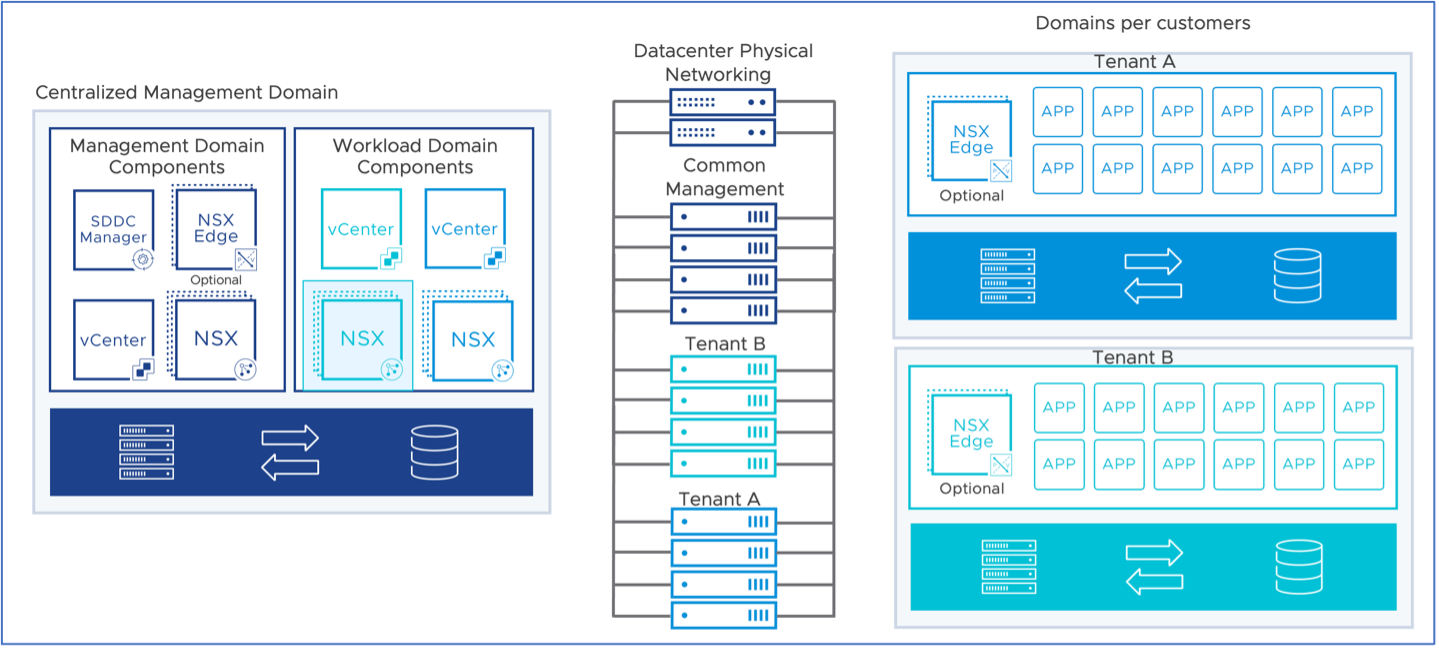
With the standard architecture model, management workloads run on a dedicated management domain, and customer workloads are deployed in separate virtual infrastructure (VI) workload domains. Each workload domain is managed by a separate vCenter Server instance which provides for scalability and allows for autonomous licensing and lifecycle management.
 Workload Domains
Workload Domains
The vCenter and NSX management components of a workload domain are deployed within the management domain, ensuring separation between management and workloads. This blog will primarily focus on isolated workload domains. With this release, each workload domain can be configured to use either a shared SSO instance with the management domain or an isolated SSO instance.
In the new architecture model, the partner manages the entire set of workload domains using a single central management domain. This eliminates the need to deploy multiple VCF environments for each customer, as was the case in the previous consolidated architecture model.
The Standard Architecture – Isolated Workload Domain
The isolated workload domain feature now allows for the option to either join an existing or create a new single sign-on (SSO) domain during workload domain deployment. In this deployment, the vCenter SSOs are no longer in an enhanced linked mode, enabling easier scalability up to 24 domains and 1000 hosts per VCF instance.
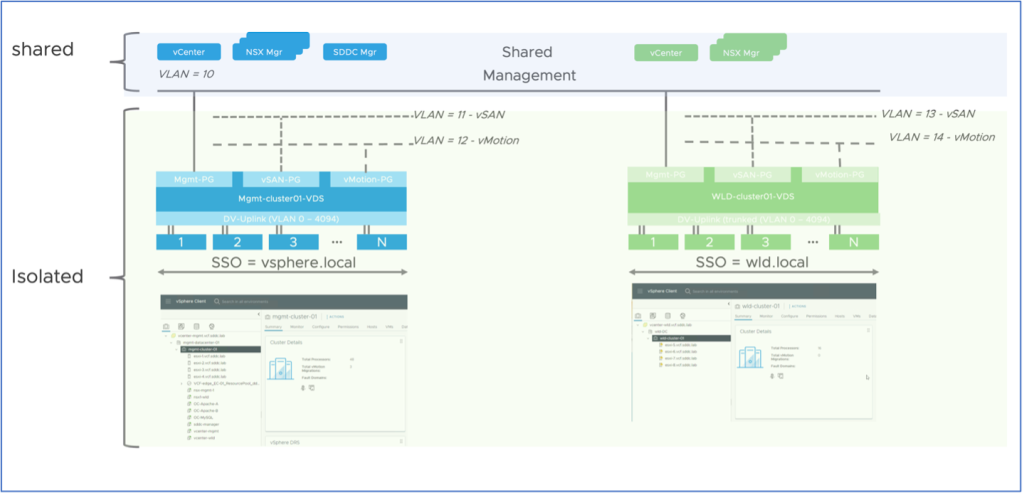 Isolated Workload Domain
Isolated Workload Domain
With this release, the management traffic continues to be shared across all workload domains. However, the provider now can separate VLANs for vSAN and vMotion traffic per workload domain by creating new separate virtual distributed switches as part of the workload domain deployment process. This feature works effectively for provider-managed services as it keeps the customer’s workload traffic separate, leveraging the out-of-the-box capability.
To create full tenant isolation in the Management Domain, Cloud Solution Providers must enable NSX Distributed Firewall (DFW) rules for Isolated Workload Domain workloads and management VMs (customer’s vCenter and NSX Manager) in order to secure the traffic between the customer’s workload domains and the management domain. The provider can leverage the instructions by referring to the NSX Admin guide. We will cover in-depth technical guidance in the follow up blog.
In a workload domain per customer standard architecture, it is not possible contractually to provide customers access of the SDDC Manager since it manages many customer workloads. The Cloud Service Provider must ensure that the customer’s cloud admin is granted required reduced level of administrative access to their vCenter server and NSX Manager and workload domains, enabling them to perform all day 2 activities except LCM (Lifecycle Management).
With the release of VMware Cloud Foundation 5.0, Cloud Solution Providers can leverage the following key advantages
- Scalable Architecture supporting up to 24 workload domains.
- Optimized CapEx by consolidating infrastructure.
- Easy onboarding of customers running 10s to 100s of VMs in minutes due to SDDC Manager’s ability to deploy customer environment v/s Cloud Build which is much more complicated and time-consuming.
- Reduction in VCF instance sprawl
- Increased operational productivity by managing fewer VCF instances.
- Most of the upgrade/patching activities can be performed simultaneously across many customer environments.
- Streamlined upgrade cycles and processes without the Enhanced Linked Mode (ELM)
Conclusion: For Cloud Service Provider aiming to deliver scalable, efficient, and resilient cloud solutions, VMware Cloud Foundation’s standard architecture presents a compelling solution. With its unified infrastructure management, elastic scalability, high availability, multi-tenancy support, and simplified lifecycle management, VCF empowers CSPs to optimize their offerings, enhance customer experiences, and stay ahead in the competitive cloud market.
Additional Resources
Remember, to get the latest updates, check this blog regularly, you also can find us on Slack, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn as well as many demo videos and enablement YouTube, especially our Feature Fridays series!
