As we enter into 2024, the adoption of AI in fields like cybersecurity marks a significant shift in business operations worldwide, reflecting greater reliance on digital and cloud technologies. AI has become critical in reevaluating and bolstering security against sophisticated cyber threats, offering innovative defenses that enhance cybersecurity efficiency and effectiveness. This move towards AI-powered solutions is key in fighting cyber risks, underlining AI’s transformative role in various industries, especially in cybersecurity.
AI’s entrance into cybersecurity presents a promising approach to overcoming these challenges, with AI-enabled platforms strengthening cybersecurity defenses against diverse threats. Utilizing big data and contextual analysis, AI helps detect cybercrime patterns, providing early defense against phishing and social engineering.
The integration of AI into cybersecurity is a reflection of the broader interest in AI technologies across various sectors. As cyber threats evolve, the need for smarter, more accurate, and more capable protections becomes evident. The MixMode State of AI in Cybersecurity Report 2024 highlights this trend, showing a significant increase in AI adoption for cybersecurity purposes. This growing reliance on AI underscores its potential to transform the cybersecurity landscape, offering innovative solutions to protect against the ever-changing nature of cyber threats.
“AI is a game-changer for cybersecurity, as it can automate and augment the detection and response capabilities of security teams, as well as reduce the noise and complexity of security operations,” said John Keister, CEO of MixMode. “However, AI also poses new challenges and risks, such as the threat of AI being used for adversarial attacks and the need for specialized operator skills. MixMode understands the complexity of AI and delivers automated capabilities to revolutionize the cybersecurity landscape through our patented self-learning algorithm that can detect threats and anomalies in real-time at high speed and scale. This helps enterprises rapidly recognize new malware and insider risks to help strained security teams automate mundane tasks and focus on higher-level defenses.”
Types of Attack Threats
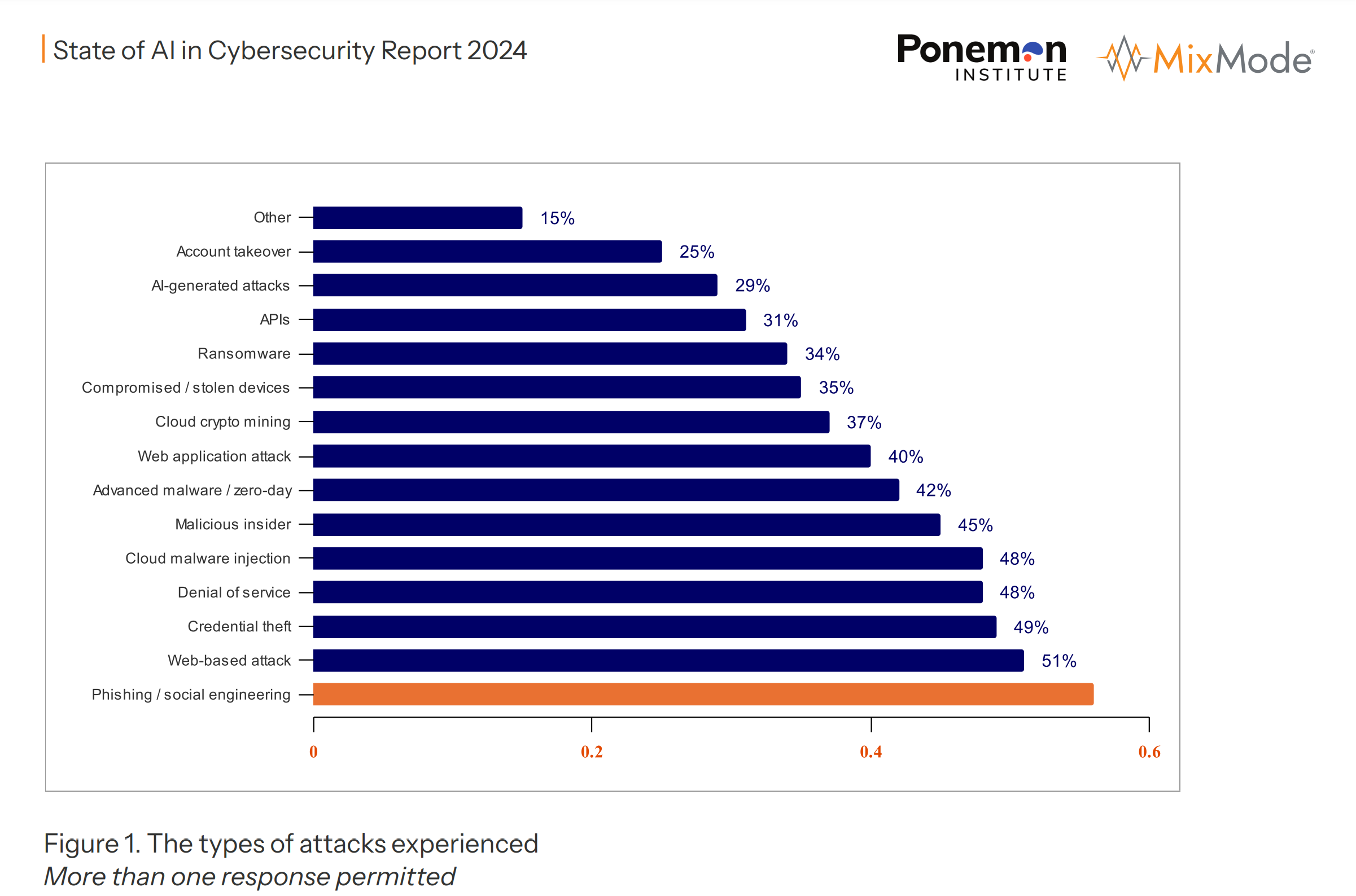
A recent infographic details the spectrum of cyber threats faced by organizations, summarizing the key findings and percentages.

- Phishing / Social Engineering (51%): The most common attack vector where attackers deceive individuals into providing confidential information or performing actions that compromise security.
- Web-based Attack (49%): Attacks that occur on websites, often exploiting browser vulnerabilities or flaws in web applications.
- Credential Theft (48%): The unauthorized access and extraction of usernames and passwords.
- Denial of Service (48%): Attacks intended to shut down a network or service, making it inaccessible to its intended users.
- Cloud Malware Injection (45%): Inserting malicious software into a cloud service’s software or hardware.
- Malicious Insider (42%): Threats that come from individuals within the organization, such as employees or contractors, who have inside information concerning the organization’s security practices, data, and computer systems.
- Advanced Malware / Zero-day (42%): Sophisticated malware that exploits unknown or unpatched vulnerabilities (zero-days) in systems.
- Web Application Attack (40%): Attacks targeting vulnerabilities in web applications to steal data, deface websites, or compromise servers.
- Cloud Crypto Mining (37%): Unauthorized use of someone else’s cloud computing resources to mine cryptocurrency.
- Compromised / Stolen Devices (35%): Incidents where devices containing organizational data are lost or stolen.
- Ransomware (34%): A type of malware that encrypts a victim’s files, with the attacker then demanding a ransom from the victim to restore access to the data upon payment.
- APIs (31%): Exploits of vulnerabilities in application programming interfaces (APIs), which can lead to unauthorized access and data breaches.
- AI-generated Attacks (29%): Cyber attacks generated or enhanced by artificial intelligence, increasing their complexity and effectiveness.
- Account Takeover (25%): Unauthorized access and control of an individual’s account.
- Other (15%): This category includes less common attacks not specifically categorized above.
The report suggests that phishing and social engineering are the leading concerns for cybersecurity, with more than half of the respondents having experienced such attacks. It also highlights the prominence of web-based attacks and the rising threat from AI-generated attacks.
Ways to Thwart the Attackers
To effectively leverage AI in preventing cybersecurity threats, organizations need to implement a multi-faceted strategy that involves the following steps:
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: AI tools must be designed to continuously learn and adapt to new threats. They should be trained on the latest datasets that include recent attack vectors, ensuring they can recognize and respond to evolving threats.
- Behavioral Analysis: AI should be utilized to analyze behavior patterns of network traffic and user activity to identify anomalies that could indicate a security threat, such as unusual login times or data access patterns.
- Automated Threat Detection: Implement AI systems that can automatically detect threats in real time, allowing for immediate response to potential breaches. This includes the detection of zero-day vulnerabilities, phishing attempts, and other sophisticated attacks.
- Predictive Analytics: Use AI for predictive analytics to foresee potential vulnerabilities and threats before they are exploited. By understanding trends and patterns, AI can predict which systems or data are most at risk.
- Incident Response Automation: Develop AI-driven tools that not only detect threats but also initiate automated responses to mitigate damage. This could involve isolating affected systems, blocking malicious IP addresses, or revoking compromised user credentials.
- Integration and Collaboration: AI tools should be integrated into the broader security ecosystem, allowing for seamless collaboration with other security solutions such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint security software.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: Employ AI to analyze threat intelligence from various sources and share insights across platforms and organizations, enhancing the collective defense against cyber threats.
- Data Privacy Compliance: Ensure that AI tools are compliant with data privacy laws and regulations. This includes training AI systems to handle sensitive data appropriately and to respect user privacy.
- Robust Testing and Validation: Regularly test and validate AI tools to ensure they are effective against known threats and to identify any potential weaknesses in the system.
- Human Oversight: Maintain human oversight over AI tools to provide context that AI may not fully understand, to make ethical decisions, and to intervene when necessary.
- Training and Awareness: Train staff to work effectively with AI tools and to understand their capabilities and limitations. Increase awareness about the importance of cybersecurity and the role of AI in protecting against threats.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate sufficient resources, including budget and personnel, to support the development and maintenance of AI tools in cybersecurity.
By taking these steps, organizations can fortify their defenses against the increasingly sophisticated landscape of cyber threats. AI preventive tools, when properly implemented and supported, can significantly reduce the risk of successful cyber attacks.
As we navigate the complexities of the digital age, the role of AI in cybersecurity will continue to expand. With global cybersecurity spending projected to rise significantly, the deployment of AI technologies is set to become more prevalent, marking a new era in the fight against cybercrime. This evolution points to a future where AI-driven security solutions not only complement traditional defenses but become central to the strategic planning and implementation of cybersecurity measures.
By Gary Bernstein

